Beginner guide to python Folium module to integrate google earth engine
Published on Apr 12, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 18504 views
Folium makes it easy to visualize data that’s been manipulated in Python on an interactive leaflet map.
Calculate NDVI from Sentinel-2 with Python API
Published on May 07, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 12404 views
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) quantifies vegetation by measuring the difference between near-infrared (which vegetation strongly reflects) and red light (which vegetation absorbs).
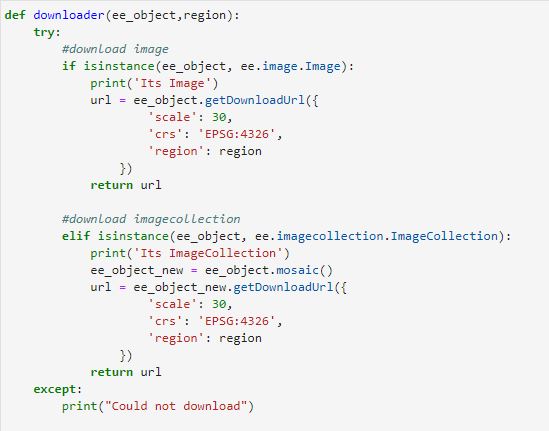
Export Google Earth Engine Images directly to your computer.
Published on Apr 11, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 11912 views
Export images, image collection, map tiles from Google Earth Engine collection directly to your computer.
Google Earth Engine tip 1 (clipping)
Published on May 26, 2021 | Bikesh Bade | 11806 views
Google Earth Engine (GEE) Tips provide a foundation to quickly begin learning and using GEE. If you are new to GEE, you will want to know small and handy tips.
Interactive web mapping with Django and Google Earth Engine
Published on May 03, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 11580 views
There are several ways to use GEE and each one has its advantages and disadvantages. In this example, GEE is used for web mapping with python Django.
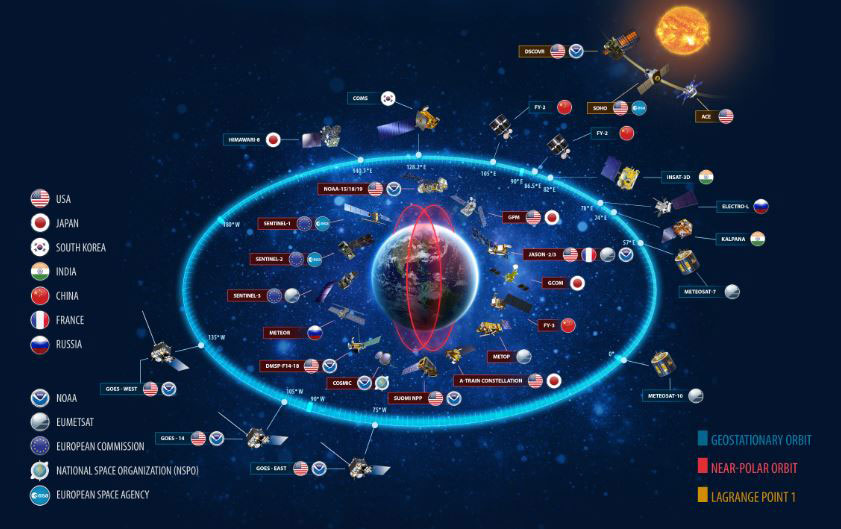
Awesome facts about Satellites
Published on May 20, 2021 | Bikesh Bade | 10852 views
Sputnik 1 was the first satellite in space. The Soviet Union launched it in 1957.
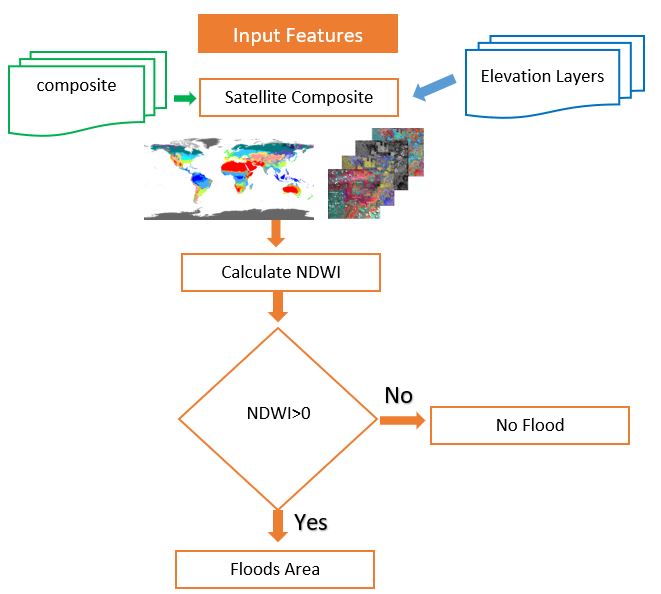
All you need to know about NDWI: Normalized Difference Water Index
Published on May 12, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 9976 views
The Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) is remote sensing derived index estimating the leaf water content at the canopy level.
Google earth engine with python
Published on May 07, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 9429 views
In addition to the web-based IDE Google Earth Engine also provides a Python API that can be used on your local machine.
Geo-pandas data frame to GEE feature collection using Python
Published on Apr 27, 2020 | Bikesh bade | 7708 views
The simplest way to convert shapefile, CSV it into ee.FeatureCollection is to infuse the Geopandas data frame with GEE python API.
NDVI time series with Google Earth Engine
Published on Sep 19, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 7530 views
Time series animations of Earth observation imagery are captivating and engaging. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to generate an animated GIF.
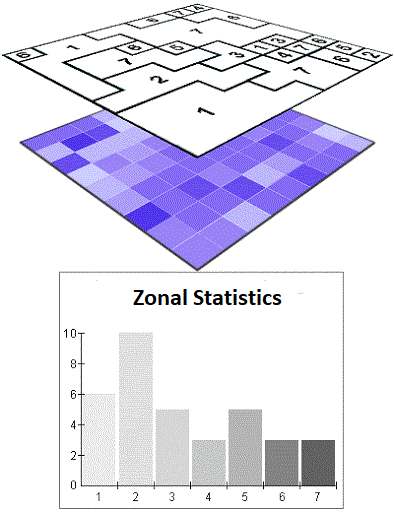
Calculate Zonal Statistics and export as CSV
Published on Jul 10, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 7233 views
Get statistics in each zone of the image or image collection in google earth engine and export the data in CSV. Statistics are simple tools that help us for a better understanding of our images. Spatial statistics is one of the most rapidly growing areas of statistics.
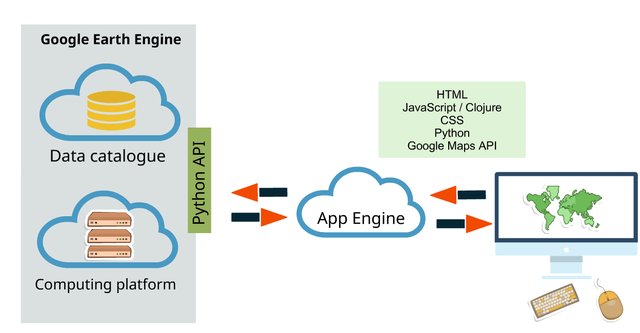
Introduction to the Google Earth Engine Python API
Published on Apr 13, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 7151 views
This tutorial will go over how to set up the API on your local machine as well as some basic Python scripts utilizing the Google Earth Engine Python API
Normalized Difference Snow Index (NDSI)
Published on May 17, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 6796 views
NDSI is a measure of the relative magnitude of the reflectance difference between visible (green) and shortwave infrared (SWIR).
All you need to know about NDVI
Published on May 07, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 6589 views
The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index is a simple indicator of photosynthetically active biomass or, in layman’s terms, a calculation of vegetation health.
Google Earth Engine as WMS Layer - Using Python API
Published on Apr 02, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 5611 views
The Python API provides a programmatic and flexible interface to Earth Engine for automating batch processing tasks, and leveraging the power of the command line.