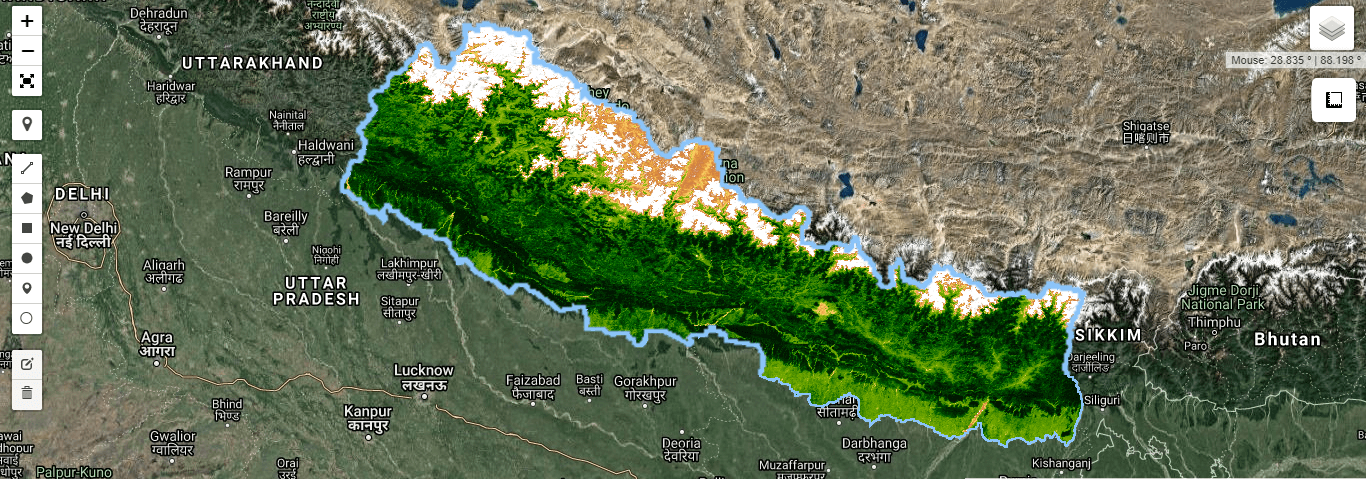
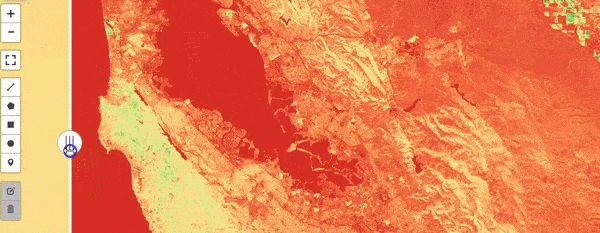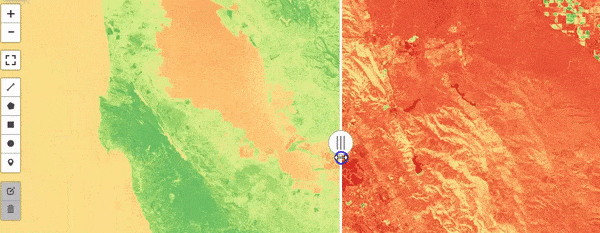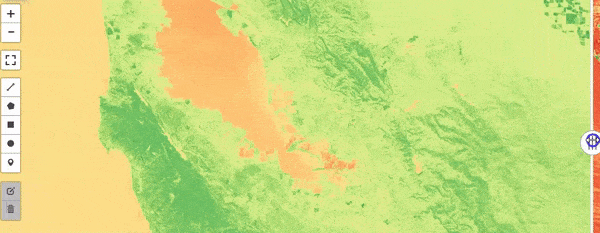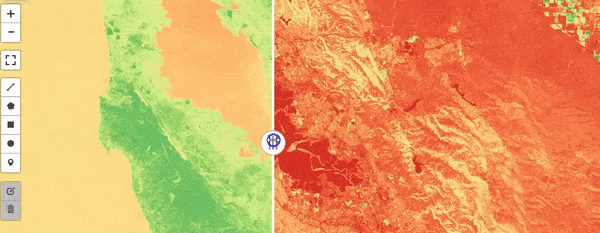
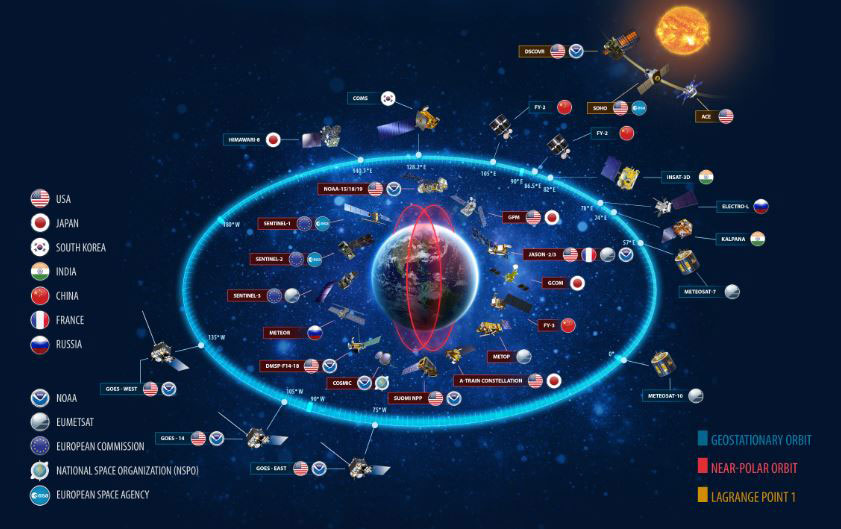
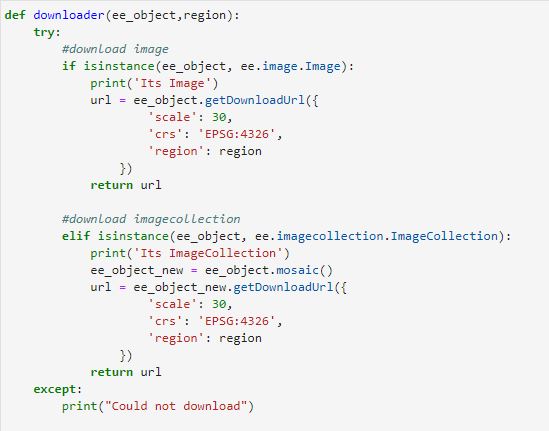
Google Earth Engine as WMS Layer - Using Python API
Published on Apr 02, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 5989 views
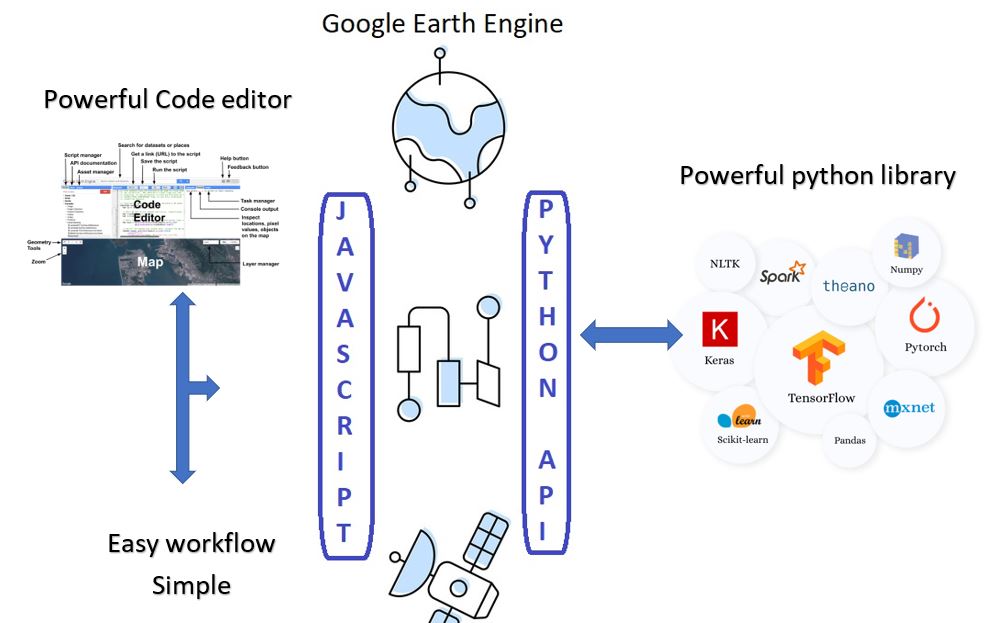
The Python API provides a programmatic and flexible interface to Earth Engine for automating batch processing tasks, and leveraging the power of the command line.
Google Earth Engine: Disadvantages and Limitation
Published on Apr 27, 2022 | Bikesh Bade | 5607 views
As Google Earth Engine is getting popular in geoscience and data computation, there are a few things that need to consider before you deep dive. This blog will highlight some of the GEE's limitations and disadvantages. Importantly, Google Earth Engine is free only for non-commercial, non-production use, This means its sole purpose is to serve the educational professional, students, and the nonprofit organization.
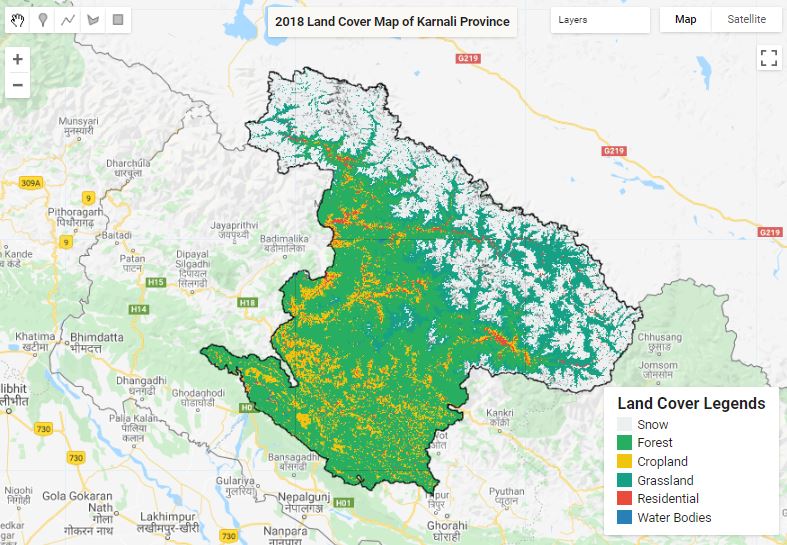
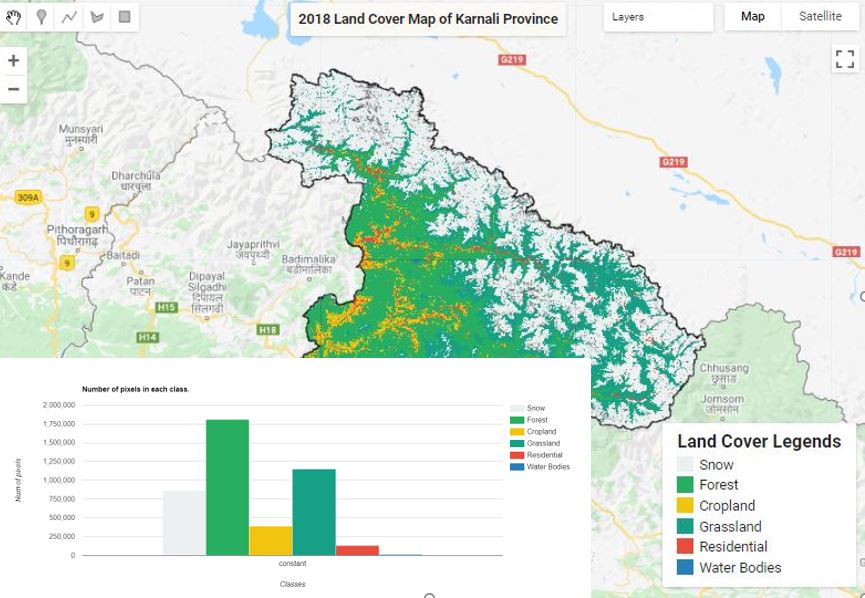
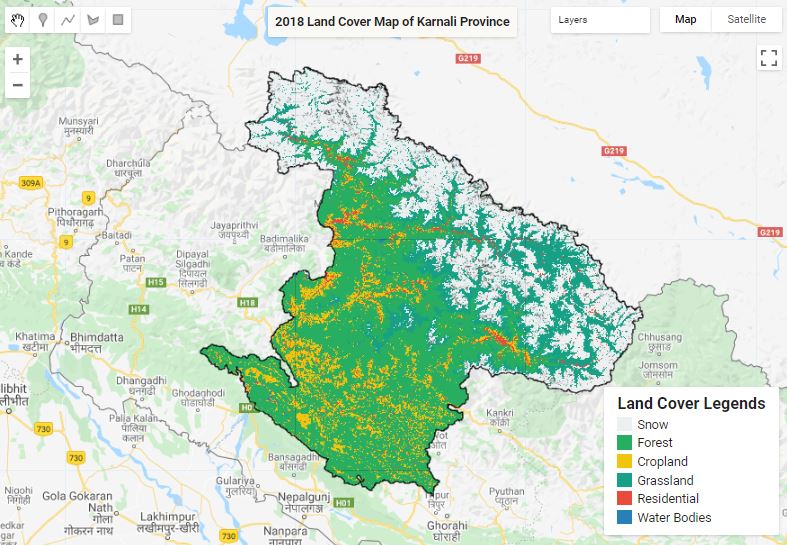
Land Cover Mapping - Part 1
Published on May 31, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 5467 views
The surface of the Earth is continuously changing at many levels; local, regional, national, and global scales. Changes in land use and land cover are pervasive, rapid, and can have significant impacts on people, the economy, and the environment.
Chirps Precipitation to Excel - GEE and Pandas
Published on Apr 29, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 5430 views
Extract Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station data (CHIRPS) is a 30+ year quasi-global rainfall dataset using Google earth engine API and convert it into. Excel and charts using Python Pandas data frame.
Supervised Classification in GEE
Published on May 10, 2020 | Bikesh bade | 5251 views
Supervised classification is the technique most often used for the quantitative analysis of remote sensing image data.
Extract CHIRPS rainfall data in excel for given survey points
Published on Nov 28, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 5206 views
Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station data (CHIRPS) is a 35+ year quasi-global rainfall data set. These tutorials provide a brief idea on how to extract the rainfall data for a given survey point from the CHIRPS global rainfall data set.
Google earth engine Detail comparison between Python and JavaScript
Published on Apr 13, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 5097 views
Both the Python and JavaScript APIs access the same server-side functionality, but it is different in the syntax and the way we digest.
All you need to know about EVI
Published on May 11, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 4860 views
EVI is similar to Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and can be used to quantify vegetation greenness. However, EVI corrects for some atmospheric conditions and canopy background noise and is more sensitive in areas with dense vegetation.
ESRI 10m Land Cover 2020 in GEE
Published on Jul 19, 2021 | Bikesh Bade | 4589 views
ESRI 10-meter resolution map of Earth’s land surface from 2020 with High-resolution, open, accurate, comparable, and timely land cover maps in GEE
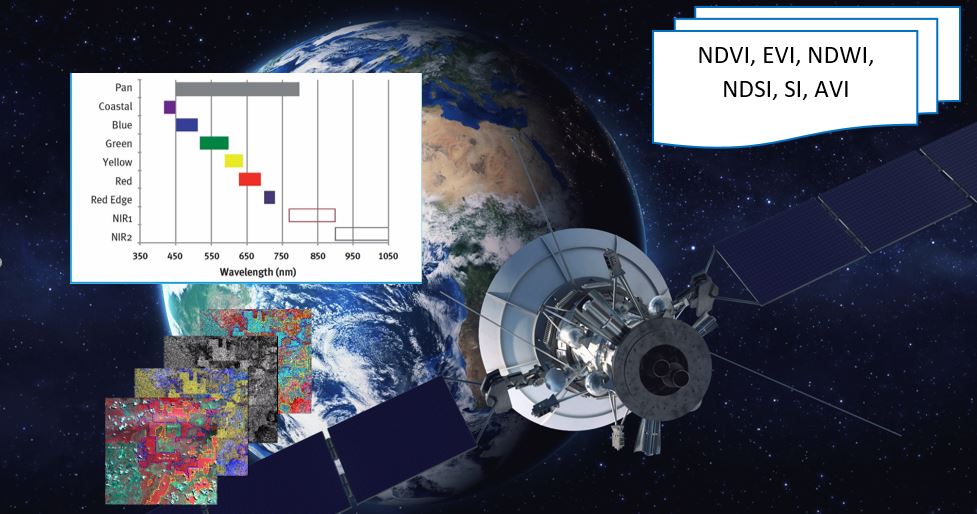
Most used spectral Indices with free satellite data
Published on May 14, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 4584 views
Today many different indices exist and each one has its own significance in the study. Here are the most popular indices that be calculated from free data satellites.
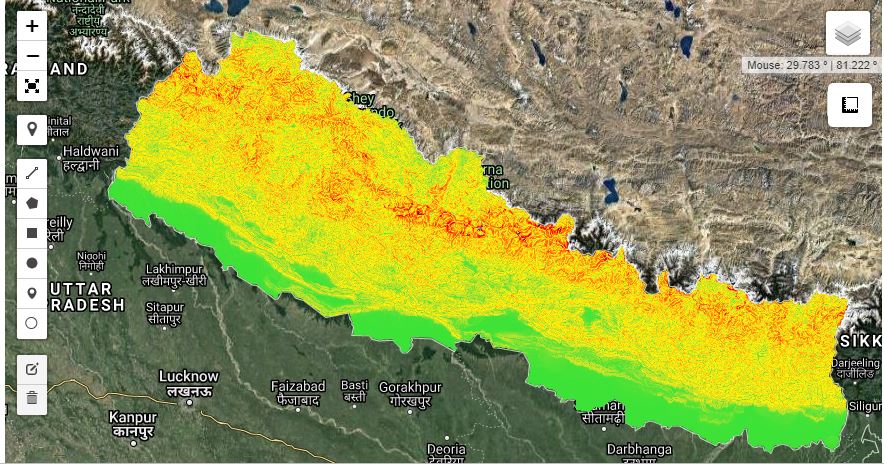
Generate Slope Elevation data from SRTM - Python API
Published on Apr 11, 2020 | Bikesh bade | 4477 views
Digital elevation data is an international research effort that obtained digital elevation models on a near-global scale. This SRTM V3 product (SRTM Plus) is provided by NASA JPL at a resolution of 1 arc-second (approximately 30m).
Land Cover Mapping - Part 4 (Analyze Statistics)
Published on Jun 08, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 4272 views
Statistics are simple tools that helps us for a better understanding of our images. Spatial statistics is one of the most rapidly growing areas of statistics.
Land Cover Mapping - Part 3 (Validation)
Published on Jun 04, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 4179 views
The surface of the Earth is continuously changing at many levels; local, regional, national, and global scales. Changes in land use and land cover are pervasive, rapid, and can have significant impacts on people, the economy, and the environment.
Calculate NDVI and export
Published on May 19, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 4087 views
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) quantifies vegetation by measuring the difference between near-infrared (which vegetation strongly reflects) and red light (which vegetation absorbs).
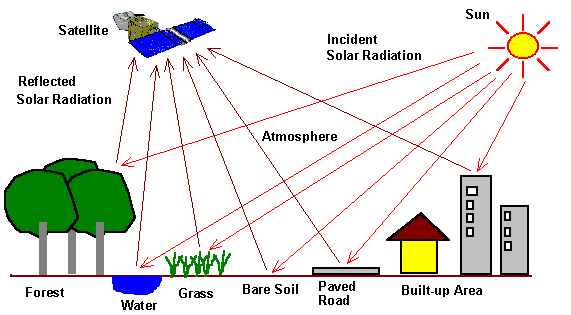
Google Earth Engine Image Pre-processing : Background and methods Part I
Published on Apr 19, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 4037 views
While using remote sensing data several pre-processing steps can be applied that aim at removing artifacts from the images that are not related to the actual reflectance of the land cover such as sensor effects, atmospheric, and illumination conditions.