Topographic illumination correction for Sentinel 2 - Python API
Published on Apr 26, 2020 | Bikesh Bade | 3547 Views
In mountain areas varying illumination conditions related to sun position, slope, and aspect result in variations of the reflectance within the same land cover type and e.g. the same forest type on a sunlit slope shows a different reflectance on a shaded slope. This signal-to-noise ratio can be reduced by performing a topographic illumination correction that adjusts differences in solar irradiance related to slope and aspect, resulting in an image that approximates reflectance values that would be recorded over a flat surface.
Different approaches exist for the topographic illumination correction and they can be grouped into three categories:
1) Empirical methods,
2) physical methods, and
3) semi-empirical methods.
We did not implement any of the empirical methods in the GEE image pre-processing tool as it can reduce accuracies. The two other approaches additionally use a digital elevation model (DEM) for the topographic correction of the images. Before correcting illumination in the image, first, we have to calculate the illumination condition. The following Function to calculate illumination condition is provided by Patrik Burns and Matt Macander.
𝐼𝐿 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑖𝑠 ) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑍) ⋅ 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑠) + 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑍) ⋅ 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑠) ⋅ 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑎 − 𝑎′) Calculation of the illumination condition (IL) for each pixel at the time of the image acquisition using a DEM, with 𝑖𝑠 = incident angle with respect to the surface normal Z = solar zenith angle (incident angle for a horizontal surface, provided by the sensor metadata s = terrain slope calculated from the DEM a = solar azimuth (provided by the sensor metadata) a’ = terrain aspect (azimuth) calculated from the DEM
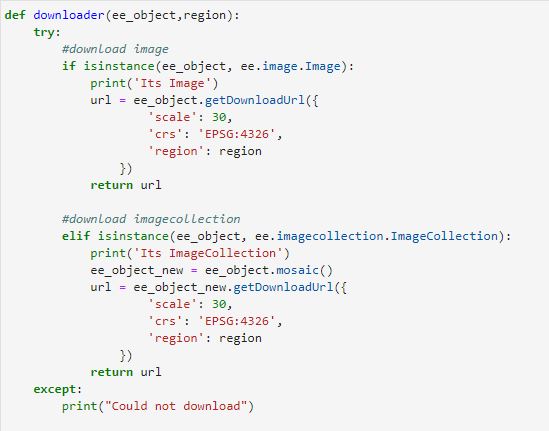
To calculate the illumination condition in the GEE using python API first you have to setup python environment in your local computer.
Set up Python API for GEE and continue following
Step 1
The Python API package is called ee. It must also be initialized for every new session and script. and import other necessary modules
# import Google earth engine module import ee #Authenticate the Google earth engine with google account ee.Initialize() #python moduel for gee import geetools #python math module import math
Step 2
Get Terrian Layer for DEM
# get terrain layers
dem = ee.Image("USGS/SRTMGL1_003")
Step 3
Create a Python function to calculate the illumination condition:
# Function to calculate illumination condition (IC). Function by Patrick Burns def illuminationCondition(img): # Extract image metadata about solar position SZ_rad = ee.Image.constant(ee.Number(img.get('MEAN_SOLAR_ZENITH_ANGLE'))).multiply(3.14159265359).divide(180).clip(img.geometry().buffer(10000)) SA_rad = ee.Image.constant(ee.Number(img.get('MEAN_SOLAR_AZIMUTH_ANGLE')).multiply(3.14159265359).divide(180)).clip(img.geometry().buffer(10000)) # Creat terrain layers slp = ee.Terrain.slope(dem).clip(img.geometry().buffer(10000)) slp_rad = ee.Terrain.slope(dem).multiply(3.14159265359).divide(180).clip(img.geometry().buffer(10000)) asp_rad = ee.Terrain.aspect(dem).multiply(3.14159265359).divide(180).clip(img.geometry().buffer(10000)) # Calculate the Illumination Condition (IC) # slope part of the illumination condition cosZ = SZ_rad.cos() cosS = slp_rad.cos() slope_illumination = cosS.expression("cosZ * cosS", {'cosZ': cosZ, 'cosS': cosS.select('slope')}) # aspect part of the illumination condition sinZ = SZ_rad.sin() sinS = slp_rad.sin() cosAziDiff = (SA_rad.subtract(asp_rad)).cos() aspect_illumination = sinZ.expression("sinZ * sinS * cosAziDiff", {'sinZ': sinZ, 'sinS': sinS, 'cosAziDiff': cosAziDiff}) # full illumination condition (IC) ic = slope_illumination.add(aspect_illumination) # Add IC to original image img_plus_ic = ee.Image(img.addBands(ic.rename('IC')).addBands(cosZ.rename('cosZ')).addBands(cosS.rename('cosS')).addBands(slp.rename('slope'))) return img_plus_ic
The next step is to correct the illumination condition in the GEE using python is to create the function as follows:
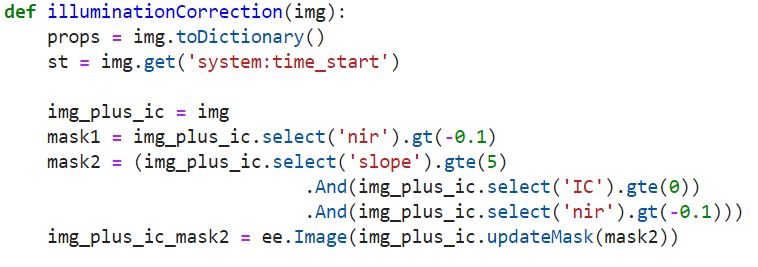
# Function to apply the Sun-Canopy-Sensor + C (SCSc) correction method to each def illuminationCorrection(img): props = img.toDictionary() st = img.get('system:time_start') img_plus_ic = img mask1 = img_plus_ic.select('nir').gt(-0.1) mask2 = (img_plus_ic.select('slope').gte(5) .And(img_plus_ic.select('IC').gte(0)) .And(img_plus_ic.select('nir').gt(-0.1))) img_plus_ic_mask2 = ee.Image(img_plus_ic.updateMask(mask2)) # Specify Bands to topographically correct #bandList = ee.List(['blue','green','red','nir','swir1','swir2']) bandList = ['blue','green','red','nir','swir1','swir2'] compositeBands = img.bandNames() nonCorrectBands = img.select(compositeBands.removeAll(bandList)) geom = ee.Geometry(img.get('system:footprint')).bounds().buffer(10000) def apply_SCSccorr(band): method = 'SCSc' out = (ee.Image(1).addBands(img_plus_ic_mask2.select('IC', band)) .reduceRegion(reducer= ee.Reducer.linearRegression(2,1), geometry= ee.Geometry(img.geometry()), scale= 300, bestEffort =True, maxPixels=10000000000)) fit = out.combine({"coefficients": ee.Array([[1],[1]])}, False) #Get the coefficients as a nested list, # ast it to an array, and get just the selected column out_a = (ee.Array(fit.get('coefficients')).get([0,0])) out_b = (ee.Array(fit.get('coefficients')).get([1,0])) out_c = out_a.divide(out_b) # Apply the SCSc correction SCSc_output = img_plus_ic_mask2.expression( "((image * (cosB * cosZ + cvalue)) / (ic + cvalue))", { 'image': img_plus_ic_mask2.select(band), 'ic': img_plus_ic_mask2.select('IC'), 'cosB': img_plus_ic_mask2.select('cosS'), 'cosZ': img_plus_ic_mask2.select('cosZ'), 'cvalue': out_c }) return SCSc_output img_SCSccorr = ee.Image(list(map(apply_SCSccorr,bandList))).addBands(img_plus_ic.select('IC')) bandList_IC = ee.List([bandList, 'IC']).flatten() img_SCSccorr = img_SCSccorr.unmask(img_plus_ic.select(bandList_IC)).select(bandList) return img_SCSccorr.addBands(nonCorrectBands).setMulti(props).set('system:time_start',st)
The final step is to call the function:
def topoCorrection(collection):
#call function to calculate illumination condition
collection = collection.map(illuminationCondition)
#call function to calculate illumination Correction
collection = collection.map(illuminationCorrection)
return(collection)
# Get Sentinel-2 data
s2s =(ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2')
.filterDate(startDate,endDate) # choose your date
.filterBounds(studyArea) # choose your study area
.filter(ee.Filter.lt('CLOUDY_PIXEL_PERCENTAGE',20))
.filter(ee.Filter.lt('CLOUD_COVERAGE_ASSESSMENT',20)))
#call correcion function
s2 = topoCorrection(s2)
Responses
Iqbal
Excellent the code is working. I would like to ask. How to get the value of topograhic illumination?
- Feb 02, 2022 |